- 记录LeetCode题目笔记,汇总LeetCode解答记录
Changelog
- 2020/06/29,撰写
- 2020/11/01,完成
Overview
- LeetCode-942. 增减字符串匹配
- LeetCode-88. 合并两个有序数组组
- LeetCode-209. 长度最小的子数组
- LeetCode-201. 数字范围按位与
- LeetCode-187. 重复的DNA序列
942. 增减字符串匹配
Description
Approach 1-分治
Description
参考 leetcode-cn 官方题解。
首先考虑字符串中的第一个字母。如果 S[0] == 'I',那么只要令 A[0] = 0,就一定能满足 A[0] < A[1]。如果 S[0] == 'D',同样我们只要令 A[0] = N,就一定能满足 A[0] > A[1]。
接下来,当我们考虑 S 中剩下的 N - 1 个字母时,还剩下 N 个数可以使用,这 N 个数为 [0 .. N - 1] 或 [1 .. N]。可以发现,由于 S[0] 的值已经确定,那么剩下 S 中的 N - 1 个字母和 N 个可用的数变成了一个和原问题相同,但规模为 N - 1 的问题。即如果 S[1] == 'I',我们就令 A[1] 为剩下数中最小的那个数;如果 S[1] == 'D',我们就令 A[1] 为剩下数中最大的那个数。
我们每次会把可以使用的数的集合中的最小值或最大值取出,并放到当前的位置,因此可以使用的数的集合总是连续的,就可以非常方便的进行维护。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(N) - 空间复杂度:
O(N)
Solution
1 | class Solution { |
88. 合并两个有序数组组
Description
Approach 1-合并后排序
Description
最朴素的解法就是将两个数组合并之后再排序。这种方法没有利用两个数组本身已经有序这一点。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O((n+m)log(n+m)) - 空间复杂度:
O(1)
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
1 | public final class System { |
System.arraycopy 方法有5个入参,如上所示,从源数组 src 的第 srcPos 索引开始,复制 length 个元素到目标数组 dest,从 destPos 开始插入。下面给出一个使用示例。
1 | int[] num1 = {1,2,3}; |
Approach 2-双指针 / 从前往后
Description
一般而言,对于有序数组可以通过 双指针法 达到 O(n + m) 的时间复杂度。
最直接的算法实现是将指针 p1 置为 nums1 的开头,p2 为 nums2 的开头,在每一步将最小值放入输出数组中。
由于 nums1 是用于输出的数组,需要将 nums1 中的前 m 个元素放在其他地方,也就需要 O(m) 的空间复杂度。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n+m) - 空间复杂度:
O(m)
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
编写代码时注意代码的精简,例如
1 | if(nums1_copy[p1] < nums2[p2]){ |
可以精简为
1 | nums1[index++] = (nums1_copy[p1] < nums2[p2]) ? nums1_copy[p1++] : nums2[p2++]; |
209. 长度最小的子数组
Description
Approach 1-暴力法
Description
采用暴力求解,两重 for 循环求解。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n^2) - 空间复杂度:
O(1)
Solution
1 | class Solution { |
Approach 2-前缀和+二分查找
Description
方法一的时间复杂度是 O(n^2),因为在确定每个子数组的开始下标后,找到长度最小的子数组需要 O(n) 的时间。如果使用二分查找,则可以将时间优化到 O(logn)。
为了使用二分查找,需要额外创建一个数组 sums 用于存储数组 nums 的前缀和,其中 sums[i] 表示从 nums[0] 到 nums[i−1] 的元素和。
得到前缀和之后,对于每个开始下标 i,可通过二分查找得到大于或等于 i 的最小下标 bound,使得 sums[bound] - sums[i-1] ≥ s,并更新子数组的最小长度,此时子数组的长度是 bound−(i−1)。
因为这道题保证了数组中每个元素都为正,所以前缀和一定是递增的,这一点保证了二分的正确性。如果题目没有说明数组中每个元素都为正,这里就不能使用二分来查找这个位置了。
在很多语言中,都有现成的库和函数来为我们实现这里二分查找大于等于某个数的第一个位置的功能,比如 C++ 的 lower_bound,Java 中的 Arrays.binarySearch,C# 中的 Array.BinarySearch,Python 中的 bisect.bisect_left。
此处给出 Java 中 Arrays.binarySearch 的源码。
1 | public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) { |
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(nlogn),其中 nn 是数组的长度。需要遍历每个下标作为子数组的开始下标,遍历的时间复杂度是O(n)。对于每个开始下标,需要通过二分查找得到长度最小的子数组,二分查找得时间复杂度是O(logn),因此总时间复杂度是O(nlogn) - 空间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是数组的长度。额外创建数组sums存储前缀和。
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
Approach 3-双指针
Description
在方法一和方法二中,都是每次确定子数组的开始下标,然后得到长度最小的子数组,因此时间复杂度较高。为了降低时间复杂度,可以使用双指针的方法。
定义两个指针 start 和 end 分别表示子数组的开始位置和结束位置,维护变量 sum 存储子数组中的元素和(即从 nums[start] 到 nums[end] 的元素和)。
初始状态下,start 和 end 都指向下标 0,sum 的值为 `0。
每一轮迭代,将 nums[end] 加到 sum,如果 sum ≥ s,则更新子数组的最小长度(此时子数组的长度是 end−start+1),然后将 nums[start] 从 sum 中减去并将 start 右移,直到 sum < s,在此过程中同样更新子数组的最小长度。在每一轮迭代的最后,将 end 右移。
参见 leetcode-cn 官方题解 的动画讲解。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是数组的长度。指针start和end最多各移动 n 次 - 空间复杂度:
O(1)
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
201. 数字范围按位与
Description
Approach 1-位移操作
Description
参考 leetcode-cn 官方题解。
对于区间中数字,考虑其二进制格式,对于一系列的位,例如 [1, 1, 0, 1, 1],只要有一个零值的位,那么其位的与运算结果,都将为零。
下面对区间 [9,12] 的情况进行分析。
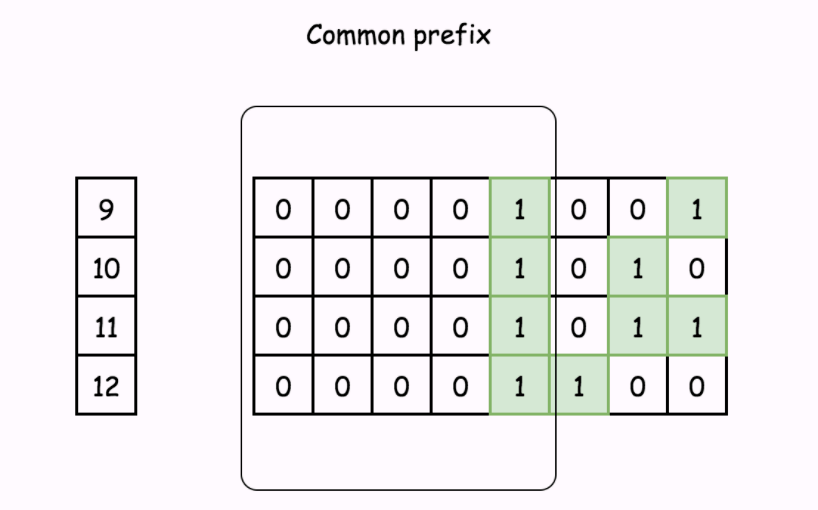
在上面的例子中,在对所有数字执行完与操作以后,剩余的部分是所有这些位字符串的公共前缀。
因此,我们可以将问题重新表述为:给定两个整数,要求我们找到它们二进制字符串的公共前缀。
采用暴力求解,两重 for 循环求解。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(1)。虽然算法中有一个循环,但是迭代次数是由整数的位数限定的,所以迭代次数是固定的。因此,算法的时间复杂度是常数级别的。 - 空间复杂度:
O(1)。不管输入是什么,内存消耗是常数的。
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
187. 重复的DNA序列
Description
Approach 1-基于HasSet
Description
将字符串中每 10 个字符串作为一个 map 容器的 key,并记录其出现的次数。若出现的次数大于1次,则输出该字符串。注意输出最终结果时,Set 到 List 的转换。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O((N-L)L),在执行的循环中,有N-L+1个长度为 L 的子字符串,这会导致O((N - L)L)时间复杂性。 - 空间复杂度:
O(N)
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |

