记录LeetCode题目笔记,汇总LeetCode解答记录
Changelog
2020/06/14,撰写
2020/06/15,添加 LeetCode-14. 最长公共前缀
2020/06/15,整理完成
Overview
1480. 一维数组的动态和 Description
Approach 1-常规求解 Analysis 本题较简单,不再赘述。
可以直接在原来数组上计算修改。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution public int [] runningSum(int [] nums) { for (int i=1 ;i<nums.length;i++){ nums[i] += nums[i-1 ]; } return nums; } }
54. 螺旋矩阵 Description
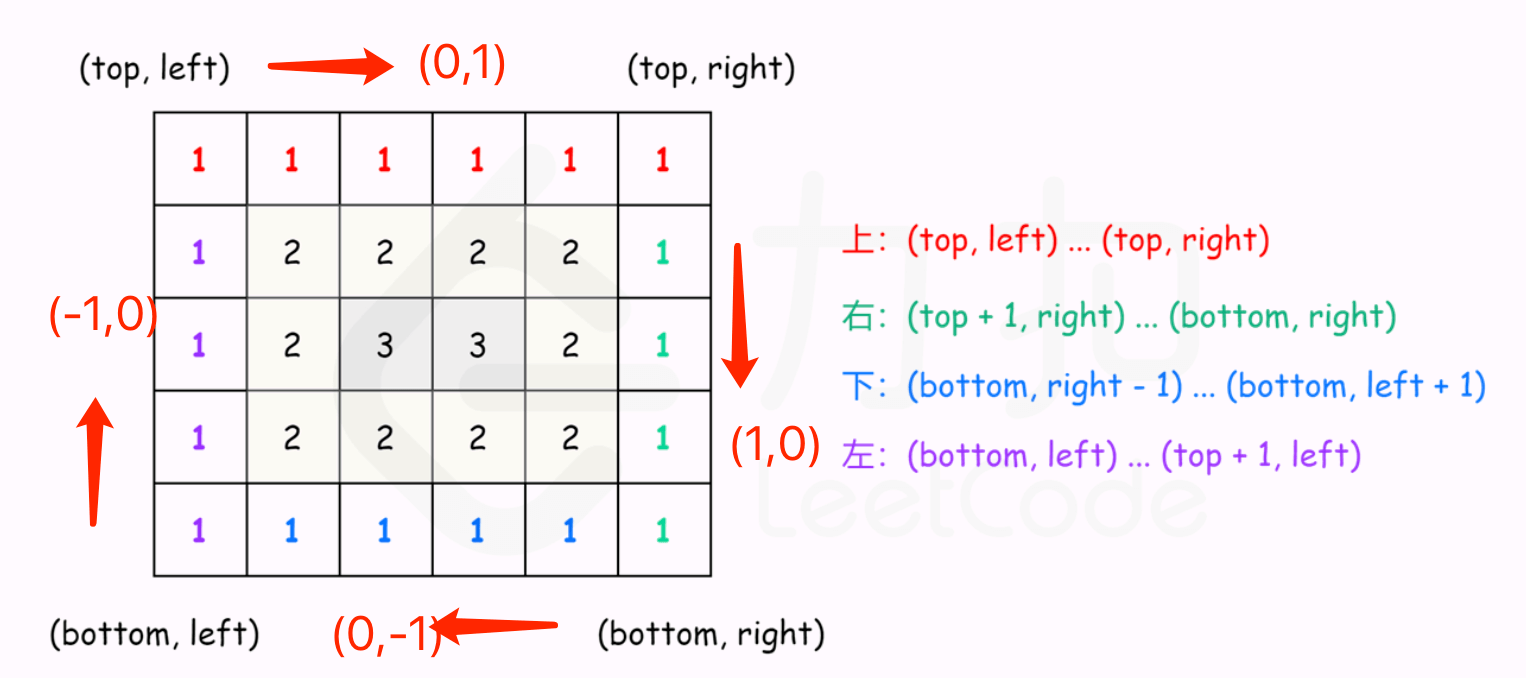
Approach 1-模拟 Analysis 模拟螺旋矩阵的路径。初始位置是矩阵的左上角,初始方向是向右,当路径超出界限或者进入之前访问过的位置时,则顺时针旋转,进入下一个方向。
判断路径是否进入之前访问过的位置,需要使用一个与输入矩阵大小相同的辅助矩阵 visited,其中的每个元素表示该位置是否被访问过。当一个元素被访问时,将 visited 中的对应位置的元素设为已访问。
如何判断路径是否结束?由于矩阵中的每个元素都被访问一次,因此路径的长度即为矩阵中的元素数量,当路径的长度达到矩阵中的元素数量时即为完整路径,将该路径返回。
代码实现过程中,可以定义一个方向数组,来表示路径模拟的4个方向,如上图中4个红色的箭头所示。
1 2 int [][] directions = {{0 ,1 },{1 ,0 },{0 ,-1 },{-1 ,0 }};
从左上角顶点到右上角顶点,数组横坐标不变,纵坐标加1,因此,方向向量为 (0,1) 从右上角顶点到右下角顶点,数组横坐标不变,纵坐标加1,因此,方向向量为 (1,0) 从右下角顶点到左下角顶点,数组横坐标不变,纵坐标减1,因此,方向向量为 (0,-1) 从左下角顶点到左上角顶点,数组横坐标减1,纵坐标不变,因此,方向向量为 (-1,0)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(mn),其中 m 和 n 分别是输入矩阵的行数和列数。矩阵中的每个元素都要被访问一次。
空间复杂度:O(mn)。需要创建一个大小为 m × n 的矩阵 visited 记录每个位置是否被访问过。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<Integer>(); if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0 ].length == 0 ){ return order; } int rows = matrix.length; int columns = matrix[0 ].length; int total = rows*columns; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [rows][columns]; int row = 0 ; int column = 0 ; int [][] directions = {{0 ,1 },{1 ,0 },{0 ,-1 },{-1 ,0 }}; int directionIndex = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<total;i++){ order.add(matrix[row][column]); visited[row][column] = true ; int nextRow = row + directions[directionIndex][0 ]; int nextColumn = column + directions[directionIndex][1 ]; if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextColumn < 0 || nextColumn >= columns || visited[nextRow][nextColumn]){ directionIndex = (directionIndex+1 )%4 ; } row = row + directions[directionIndex][0 ]; column = column + directions[directionIndex][1 ]; } return order; } }
Approach 2-按层模拟 Analysis 可以将矩阵看成若干层,首先输出最外层的元素,其次输出次外层的元素,直到输出最内层的元素。
定义矩阵的第 k 层是到最近边界距离为 k 的所有顶点。例如,下图矩阵最外层元素都是第 1 层,次外层元素都是第 2 层,剩下的元素都是第 3 层。
1 2 3 4 5 [[1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 ], [1 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 1 ], [1 , 2 , 3 , 3 , 3 , 2 , 1 ], [1 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 2 , 1 ], [1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 , 1 ]]
对于每层,从左上方开始以顺时针的顺序遍历所有元素。假设当前层的左上角位于 (top,left),右下角位于 (bottom,right),按照如下顺序遍历当前层的元素。
从左到右遍历上侧元素,依次为 (top,left) 到 (top,right)。
从上到下遍历右侧元素,依次为 (top+1,right) 到 (bottom,right)。
如果 left < right 且 top < bottom,则从右到左遍历下侧元素,依次为 (bottom,right−1) 到 (bottom,left+1)。以及从下到上遍历左侧元素,依次为 (bottom,left) 到 (top+1,left)。
遍历完当前层的元素之后,将 left 和 top 分别增加 1,将 right 和 bottom 分别减少 1,进入下一层继续遍历,直到遍历完所有元素为止。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(mn),其中 m 和 n 分别是输入矩阵的行数和列数。矩阵中的每个元素都要被访问一次。
空间复杂度:O(1)。除了输出数组以外,空间复杂度是常数。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<Integer>(); if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0 ].length == 0 ) { return order; } int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0 ].length; int left = 0 , right = columns - 1 , top = 0 , bottom = rows - 1 ; while (left <= right && top <= bottom) { for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) { order.add(matrix[top][column]); } for (int row = top + 1 ; row <= bottom; row++) { order.add(matrix[row][right]); } if (left < right && top < bottom) { for (int column = right - 1 ; column > left; column--) { order.add(matrix[bottom][column]); } for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) { order.add(matrix[row][left]); } } left++; right--; top++; bottom--; } return order; } }
59. 螺旋矩阵 II Description
Approach 1-模拟 Analysis 参考 LeetCode Notes-54. 螺旋矩阵 中方法1的思路求解。
对于数组赋值,可以使用数组元素是否为0(数组初始化元素为0)来区分该元素是否已经被赋值。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n^2),填充时候遍历了数组元素。
空间复杂度:O(n^2),需要一个 n*n 的数组来存储结果。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution public int [][] generateMatrix(int n) { int [][] arr = new int [n][n]; int [][] directions = {{0 ,1 },{1 ,0 },{0 ,-1 },{-1 ,0 }}; int directionIndex = 0 ; int total = n*n; int row = 0 ; int col = 0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=total;i++){ arr[row][col] = i; int nextRow = row + directions[directionIndex][0 ]; int nextCol = col + directions[directionIndex][1 ]; if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= n || nextCol <0 || nextCol >= n || arr[nextRow][nextCol] != 0 ){ directionIndex = (directionIndex+1 )%4 ; } row = row + directions[directionIndex][0 ]; col = col + directions[directionIndex][1 ]; } return arr; } }
14. 最长公共前缀 Description
Approach 1-横向扫描 Analysis 求解整个数组的最长公共前缀,可以
先求解前2个元素的最长公共前缀 prefix
再求解 prefix 和第3个元素的最长公共前缀,并更新 prefix
再求解 prefix 和第4个元素的最长公共前缀,并更新 prefix
…
基于上述思路,对数组元素进行横向扫描,可以求解出整个数组的最长公共前缀。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(mn),其中 m 是字符串数组中的字符串的平均长度,n 是字符串的数量。最坏情况下,字符串数组中的每个字符串的每个字符都会被比较一次。
空间复杂度:O(1)。使用的额外空间复杂度为常数。
Solutiob
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) if (strs == null || strs.length == 0 ) { return "" ; } String prefix = strs[0 ]; int count = strs.length; for (int i=1 ;i<count;i++){ prefix = longestCommonPrefix(prefix,strs[i]); if (prefix.length() == 0 ){ break ; } } return prefix; } public String longestCommonPrefix (String str1,String str2) int count = Math.min(str1.length(),str2.length()); int index = 0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<count;i++){ if (str1.charAt(i) != str2.charAt(i)){ break ; } index++; } return str1.substring(0 ,index); } }
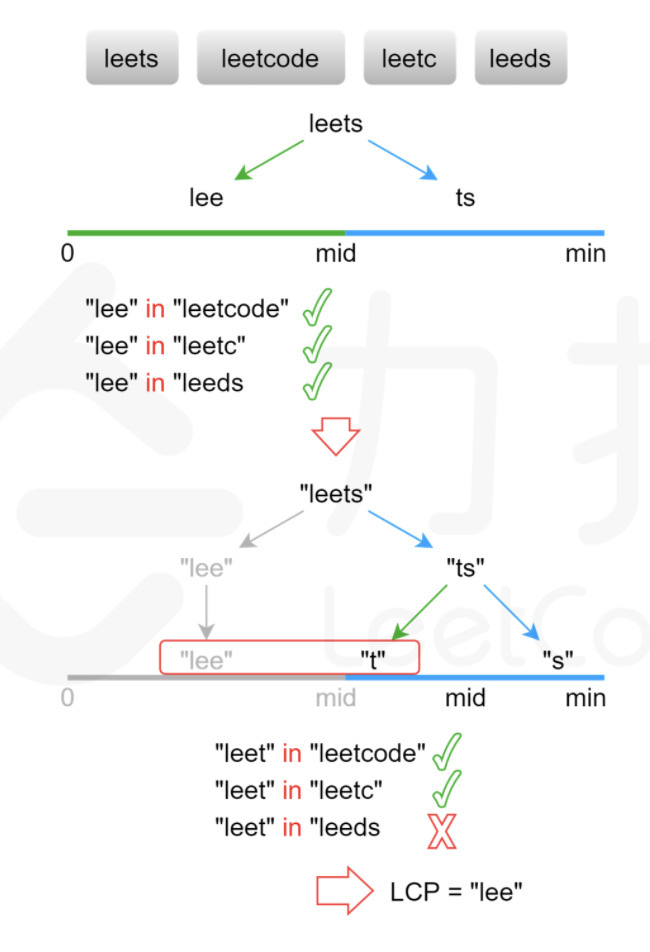
Approach 2-二分查找 Analysis 参见 leetcode-cn 官方题解。
显然,最长公共前缀的长度不会超过字符串数组中的最短字符串的长度。 用 minLength}minLength 表示字符串数组中的最短字符串的长度,则可以在 [0,minLength] 的范围内通过二分查找得到最长公共前缀的长度。每次取查找范围的中间值 mid,判断每个字符串的长度为 mid 的前缀是否相同,如果相同则最长公共前缀的长度一定大于或等于 mid,如果不相同则最长公共前缀的长度一定小于 mid,通过上述方式将查找范围缩小一半,直到得到最长公共前缀的长度。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(mn \log m)$,其中 m 是字符串数组中的字符串的最小长度,n 是字符串的数量。二分查找的迭代执行次数是 $O(\log m)$,每次迭代最多需要比较 mn 个字符,因此总时间复杂度是 $O(mn \log m)$。
空间复杂度:O(1)。使用的额外空间复杂度为常数。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution public String longestCommonPrefix (String[] strs) if (strs == null || strs.length == 0 ) { return "" ; } int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (String str:strs){ minLength = Math.min(minLength,str.length()); } int low = 0 ; int high = minLength; while (low < high){ int mid = (high - low + 1 ) / 2 + low; if (isCommonPrefix(strs,mid)){ low = mid; } else { high = mid-1 ; } } return strs[0 ].substring(0 ,low); } public boolean isCommonPrefix (String[] strs, int length) String str0 = strs[0 ].substring(0 ,length); int count = strs.length; for (int i=1 ;i<count;i++){ String str = strs[i]; for (int j=0 ;j<length;j++){ if (str0.charAt(j) != str.charAt(j)){ return false ; } } } return true ; } }
此处,对二分查找中 mid 的计算做如下说明
1 2 3 4 5 while (low < high>){ int mid = (high - low + 1 ) / 2 + low; }
不使用 mid = (low+high)/2,是因为数据相加容易产生溢出
在数组长度大于1的情况下,一般使用 mid = low + (high - low) / 2 计算
如果数组长度为1,这个时候 low=0, high=1,计算的 mid = low + (high - low) / 2 = 0,会造成无限循环。如果使用 mid = (high - low + 1) / 2 + low 计算,则 mid = 1 = high,在后续循环中执行 high = mid-1,从而使得 low = high,结束了 while 循环。
1300. 转变数组后最接近目标值的数组和 Description
Approach 1-排序后遍历数组 Analysis 题意可以总结为,找到某个 value 值,将大于 value 的数组元素缩小到 value,使得数组总和最接近 target。
分析题意,有如下思路
对数组进行排序。
若数组本身求和小于等于 target,则没有必要再缩小某些值了,直接返回数组的最大值即可。
否则,用 target 值除以数组长度,得到一个平均值,对平均值上下的两个整数值进行判断,并返回
于是乎,很容易有如下代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution public int findBestValue (int [] arr, int target) int max = 0 ; int value = 0 ; int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int sum = 0 ; for (int num:arr){ max = Math.max(max,num); sum += num; } if (sum <= target){ return max; } int avgValue = target/arr.length; if ((target - avgValue*arr.length) < ((avgValue+1 )*arr.length - target)){ return avgValue; } else { return avgValue+1 ; } return 0 ; } }
提交代码,会发现对于下述测试用例,计算结果并不符合预期
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 [1547 ,83230 ,57084 ,93444 ,70879 ] 71237 17422 14247
产生错误的原因是,若数组中有小于平均值的元素 arr[i],在最后在和 target 值比较时,这些元素 arr[i] 并不会被替换为平均值参与计算,因此导致了这种情况下,计算出的数组平均值并不是符合要求的 value 值。
下面对求解思路进行逻辑完善。
对数组进行排序。
若数组本身求和小于等于 target,则没有必要再缩小某些值了,直接返回数组的最大值即可。
否则,用 target 值除以数组长度,得到一个平均值 avgValue。
若计算出的平均值 avgValue,小于数组的每一个元素,则说明数组的每一个元素值都会被替换。此时结果一定是平均值上下的两个整数中的一个。 若不满足步骤4,则对数组进行遍历
对于已经排序好的数组,分别取 value 为数组中的第 i 个元素值,直到发现 sum >= target。
此时记录第 i 个元素左边的元素和为 sumLeft,那么如果 i 和 i 右边的数字全部变成 ans = (target - sumLeft)/(n - i),这个时候总和就是 sumLeft + ans*(n - i) = target。
这个时候计算出的 ans 就是最后要返回的结果,对其上下两个临近的整数值判断并返回正确结果即可。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O((N),进行了数组遍历
空间复杂度:O(1)。
在 leetcode-cn 平台测试,方法1执行用时4ms,内存消耗40MB;下述方法2执行用时32ms,内存消耗40.1MB;
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution public int findBestValue (int [] arr, int target) Arrays.sort(arr); int sumArr = 0 ; int arrLength = arr.length; for (int num:arr){ sumArr += num; } if (sumArr <= target){ return arr[arrLength-1 ]; } if (arr[0 ]*arrLength >= target){ int avgValue = target/arrLength; if ((target - avgValue*arrLength) < ((avgValue+1 )*arrLength - target)){ return avgValue; } else { return avgValue+1 ; } } int sumLeft = arr[0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<arrLength;i++){ int sum = sumLeft + arr[i]*(arrLength-i); if (sum >= target){ int ans = (target - sumLeft)/(arrLength - i); if (target - sumLeft - ans*(arrLength - i) <= (ans + 1 ) * (arrLength - i) + sumLeft - target){ return ans; } else { return ans + 1 ; } } sumLeft += arr[i]; } return 0 ; } }
Approach 2-枚举+二分查找 Analysis 分析题意可知,要返回的 value 值的取值范围在区间 [1,arrMaxNum]中,即最小值可能是1,最大值是数组元素的最大值。因此可以枚举 value 的可能取值进行求解。
当枚举到 value=x 时,我们需要将数组 arr 中所有小于等于 x 的值保持不变,所有大于 x 的值变为 x。要实现这个操作,我们可以将数组 arr 先进行排序,随后进行二分查找,找出数组 arr 中最小的比 x 大的元素 arr[i]。此时数组的和变为
arr[0] + ... + arr[i - 1] + x * (n - i)
为了加速求和操作,我们可以预处理出数组 arr 的前缀和,这样数组求和的时间复杂度即能降为 O(1)。我们将和与 target 进行比较,同时更新答案即可。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O((N + C)\log N)$,其中 N 是数组 arr 的长度,C 是一个常数,为数组 arr 中的最大值,不会超过 $10^5$。排序需要的时间复杂度为 $O(N\log N)$,二分查找的单次时间复杂度为 $O(\log N)$,需要进行 C 次。
空间复杂度:O(N)。我们需要 O(N) 的空间用来存储数组 arr 的前缀和,排序需要 O(logN) 的栈空间,因此最后总空间复杂度为 O(N)。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution public int findBestValue (int [] arr, int target) Arrays.sort(arr); int n = arr.length; int [] prefix = new int [n+1 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<n+1 ;i++){ prefix[i] = arr[i-1 ] + prefix[i-1 ]; } int ans = 0 ; int diff = target; for (int i=1 ;i<=arr[n-1 ];i++){ int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr,i); if (index < 0 ){ index = -index-1 ; } int cur = prefix[index] + (n-index)*i; if (Math.abs(cur - target) < diff){ ans = i; diff = Math.abs(cur - target); } } return ans; } }