- 记录LeetCode题目笔记,汇总LeetCode解答记录
Changelog
- 2020/02/29,撰写
- 2020/05/12,整理完成
Overview
- LeetCode-344. 反转字符串
- LeetCode-204.Count Primes
- LeetCode-506. 相对名次
- LeetCode-61. 旋转链表
- LeetCode-1389. 按既定顺序创建目标数组
344. 反转字符串
Description
编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 char[] 的形式给出。
不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组、使用 O(1) 的额外空间解决这一问题。
你可以假设数组中的所有字符都是 ASCII 码表中的可打印字符。
示例 1
输入:["h","e","l","l","o"]
输出:["o","l","l","e","h"]示例 2
输入:["H","a","n","n","a","h"]
输出:["h","a","n","n","a","H"]Approach 1
Analysis
Solution
- Java
1 | //国内版leetcode-cn |
1 | //国外版 leetcode |
- C++ 实现1:基本方法
1 | class Solution { |
- C++ 实现2:采用STL库中的
reverse()函数
template < BidirectionalIterator> void reverse (BidirectionalIterator first, BidirectionalIterator last);Reverses the order of the elements in the range [first,last).
The function callsiter_swapto swap the elements to their new locations.
1 | //国内版leetcode-cn |
1 | //国外版 leetcode |
string.begin()和 string.end()使用了迭代器操作。
- JS: 使用
myString.split("").reverse().join("")
1 | var reverseString = function(s) { |
先使用 split() 将字符串转化为数组,再调用数组的 reverse() 方法反转数组,最后使用 join() 方法将数组转化为字符串,使用Demo如下所示。
1 | var str = "LiuBaoshuai"; |
204. 计数质数
Description
统计所有小于非负整数 n 的质数的数量。
示例
输入: 10
输出: 4
解释: 小于 10 的质数一共有 4 个, 它们是 2, 3, 5, 7 。提示1
- Let’s start with a
isPrimefunction. To determine if a number is prime, we need to check if it is not divisible by any number less than n. The runtime complexity of isPrime function would be O(n) and hence counting the total prime numbers up to n would be O(n^2). Could we do better? - 判断一个数是否是质数,我们需要判断它是否可以被任意一个比它小的数字整除。因此判断一个数是否是质数的时间复杂度将是
O(n)。因此,计数质数的时间复杂度将是O(n^2)
提示2
- As we know the number must not be divisible by any number >
n/2, we can immediately cut the total iterations half by dividing only up ton/2. Could we still do better? - 考虑一个数
number的最大因数,因为num=1*num=2*p,因此,如果num可以被2整除,则p的最大值为num/2。因此,我们在判断质数的循环条件,可以从[1,num)缩减至[1,num/2)。
提示3
- Let’s write down all of 12’s factors(让我们写下数字12的所有因数分解表达式)
1 | 2 × 6 = 12 |
- As you can see, calculations of
4 × 3and6 × 2are not necessary. Therefore, we only need to consider factors up to√nbecause, ifnis divisible by some numberp, then n = p × q and since p ≤ q, we could derive thatp ≤ √n. - 可以看到,计算
4 × 3和6 × 2是没有必要的。我们只需要考虑因数小于等于√n的情况即可。因此,我们在判断质数的循环条件,可以从[1,num/2)缩减至[1,√n]。 - Our total runtime has now improved to
O(n^1.5), which is slightly better. Is there a faster approach? - 综上,我们的时间复杂度可以优化到
O(n^1.5)。那么还能继续提升优化吗?
1 | public int countPrimes(int n) { |
提示4
- The Sieve of Eratosthenes is one of the most efficient ways to find all prime numbers up to n. But don’t let that name scare you, I promise that the concept is surprisingly simple.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes 是目前计算质数最高效的方法之一。不要担心,我保证这个概念和方法时十分简单的。
- We start off with a table of n numbers. Let’s look at the first number, 2. We know all multiples of 2 must not be primes, so we mark them off as non-primes. Then we look at the next number, 3. Similarly, all multiples of 3 such as 3 × 2 = 6, 3 × 3 = 9, … must not be primes, so we mark them off as well. Now we look at the next number, 4, which was already marked off. What does this tell you? Should you mark off all multiples of 4 as well?
- 4 is not a prime because it is divisible by 2, which means all multiples of 4 must also be divisible by 2 and were already marked off. So we can skip 4 immediately and go to the next number, 5. Now, all multiples of 5 such as 5 × 2 = 10, 5 × 3 = 15, 5 × 4 = 20, 5 × 5 = 25, … can be marked off. There is a slight optimization here, we do not need to start from 5 × 2 = 10. Where should we start marking off?
- 让我们从一个包含
n个数字的列表开始。首先看下第1个数字2,我们知道2的倍数肯定不是质数,因此我们可以将它们标记为非质数。 - 之后,再看第2个数字
3,同样3的倍数也可以被标记为非质数。 - 之后,再看第3个数字
4,因为数字4是数字2的倍数,已经被标记为了非质数。因为4的倍数一定是2的倍数,即4的倍数已经被标记了,所以我们可以跳过数字4,去看下一个数字5。
提示5
- In fact, we can mark off multiples of 5 starting at 5 × 5 = 25, because 5 × 2 = 10 was already marked off by multiple of 2, similarly 5 × 3 = 15 was already marked off by multiple of 3. Therefore, if the current number is p, we can always mark off multiples of p starting at
p^2, then in increments of p: p^2 + p, p^2 + 2p, … Now what should be the terminating loop condition? - 对于数字
5的判断,此处有一个小优化项。我们真的需要从5的倍数10,15,20开始标记吗?其实是没必要的,因为数字10=2*5,15=3*5,20=4*5,它们已经被标记处理了。总结可以发现,我们从25=5*5开始判断即可。即我们开始判断的起点是p^2,后续标记为p^2 + p,p^2 + 2p,...
提示6
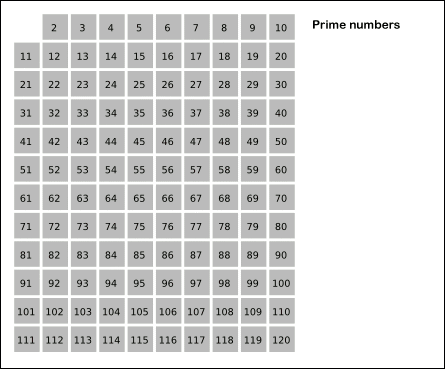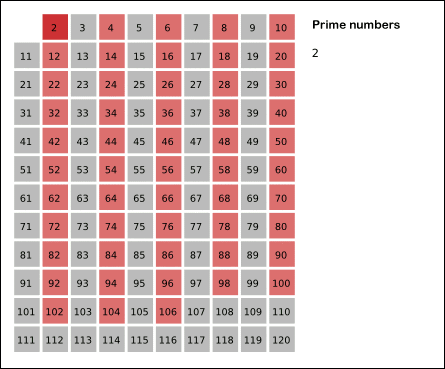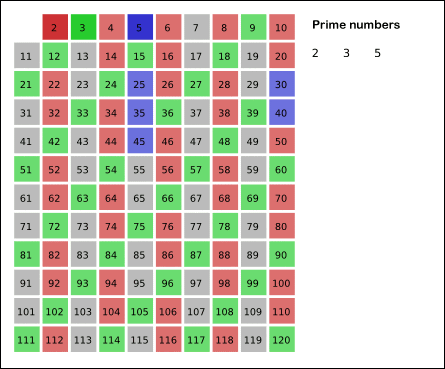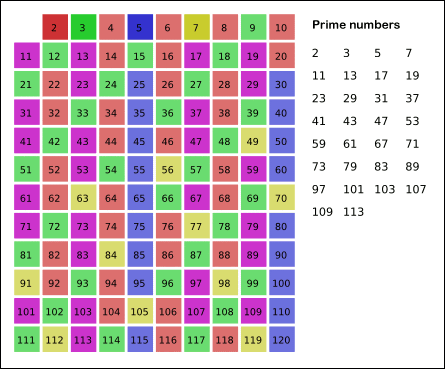
- It is easy to say that the terminating loop condition is
p < n, which is certainly correct but not efficient. - Yes, the terminating loop condition can be
p < √n, as allnon-primes ≥ √nmust have already been marked off. When the loop terminates, all the numbers in the table that are non-marked are prime. - 很容易发现,循环终止条件是
p < n,但这个终止条件仅仅是正确的,不是最高效的。 - 实际上,循环终止条件应该是是
p <= √n,因为所有大于√n的因数已经被标记处理了。 - 当上述循环判断结束后,所有没有被标记的数字就是质数。
提示7
- The Sieve of Eratosthenes uses an extra
O(n)memory and its runtime complexity isO(nlogn). For the more mathematically inclined readers, you can read more about its algorithm complexity on Wikipedia. Sieve of Eratosthenes方法的空间复杂度是O(n),时间复杂度是O(nlogn),更多数学推导可参考Wikipedia。
1 | public int countPrimes(int n) { |
Approach 1-参考题目提示使用Sieve of Eratosthenes
Analysis
参考题目提示,使用 Sieve of Eratosthenes 方法求解。
Solution
- Java
1 | public class Solution { |
506. 相对名次
Description
Approach 1-Map映射
Analysis
很自然的会想到对数组进行排序。但直接排序的话,会丢失数组原有的顺序。因此,可以使用 Map 数据结构,维护一个分数和名次的映射关系。
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
- C++
C++中,借助 pair<int,int> 数据结构实现。
1 | class Solution { |
- JS
1 | /** |
61. 旋转链表
Description
Approach 1-构造环形链表
Analysis
查看 leetcode-cn 官方题解,求解本题。
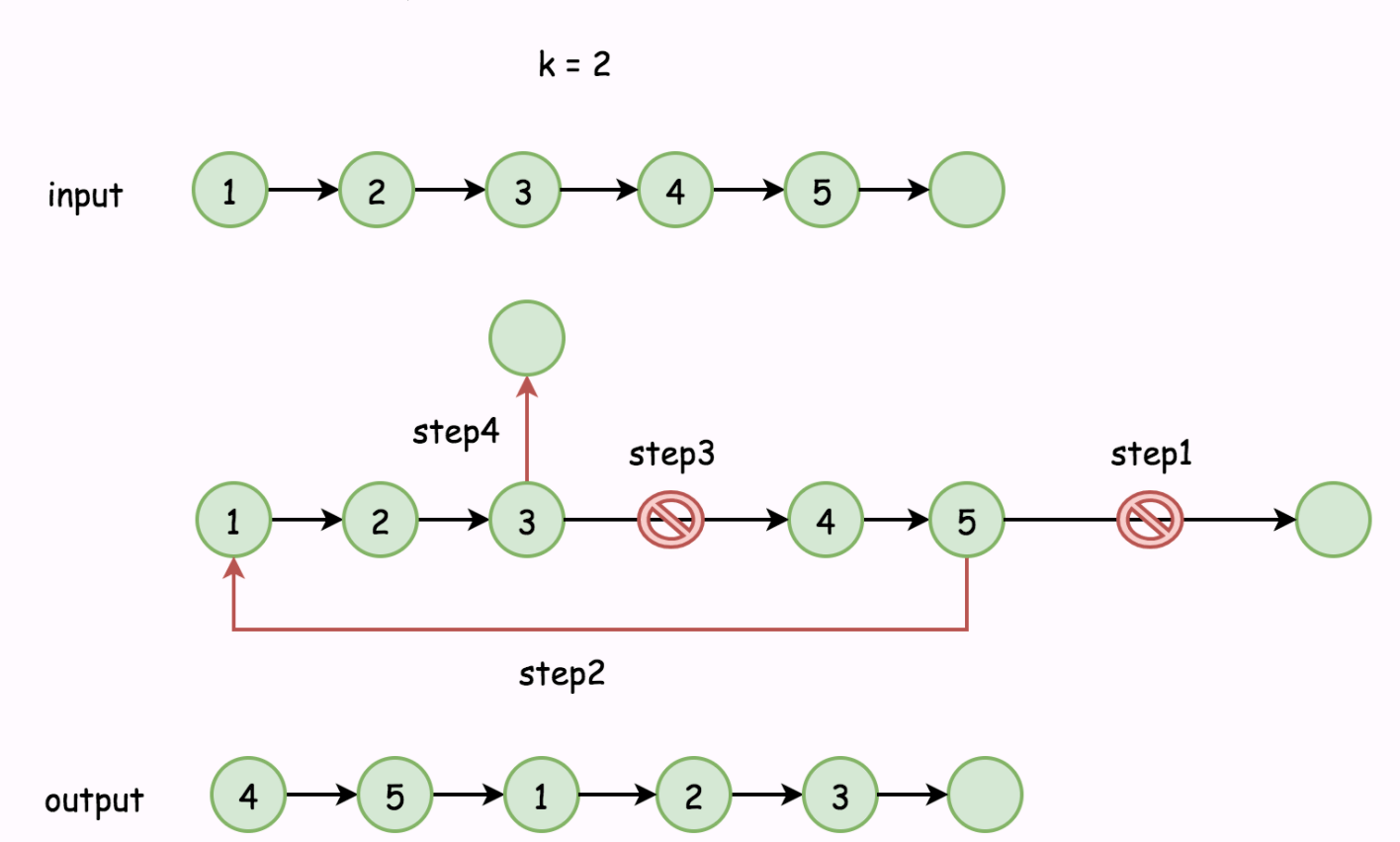
结合上图分析
- 先将链表闭合成环形链表
- 将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置,意味着链表头节点的移动
- 移动结束后,找到新的链表头节点和尾节点,并断开链表
不难发现,若移动位置小于一圈时(n<k),新的链表头节点在 n-k处,新的链表尾节点在 n-k-1 处。若移动位置大于一圈(n<k),移动一整圈对结果并无影响。
因此,可以总结如下
- 新的链表头节点在
n - k%n处 - 新的链表尾节点在
n - k%n - 1处
算法实现思路如下
- 找到旧的尾部,并将其与链表头相连
old_tail.next = head,整个链表闭合成环,同时计算出链表的长度 n - 找到新的尾部,第 (
n - k % n - 1) 个节点 ,新的链表头是第 (n - k % n) 个节点 - 断开环
new_tail.next = null,并返回新的链表头new_head。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(N),其中 N 是链表中的元素个数 - 空间复杂度:
O(1),因为只需要常数的空间
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |
1389. 按既定顺序创建目标数组
Description
Approach 1-链表实现
Analysis
- 查看题目的限制条件
0 <= index[i] <= i,可知在插入第i个元素时,索引最多为最后一个元素。 - 分析题目可知,要在当前的下标从 0 开始长度为 n 的顺序表的
i位置插入元素,就要先把原来表中区间[i, n]中的元素从全部向后移动一位,然后在i位置插入带插入的元素。 - 对于 Java 而言,可以使用
ArrayList数据结构实现,其add(int index, E element)源码如下。
可以发现,在调用 add(int index, E element),会先检查是否需要扩容。若需要的话,会将 index 及其之后的元素都向后移动一位,并将新元素插入到 idnex 处。
1 | /** |
Solution
- Java
1 | class Solution { |

