记录LeetCode题目笔记,汇总LeetCode解答记录
Changelog
2020/02/23,撰写
2020/02/28,整理完成
Overview
371. 两整数之和 Description
Approach 1-位运算 Analysis 利用位运算求解。
1 2 3 4 5 6 5 +2 =7 加法 情况1 :无进位加法 0101 0101 + 0010 XOR 0010 -------- ---------- 0111 0111
如上所示,在无进位的情况下,加法可以使用异或运算 XOR 替代。
情况2:有进位的加法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 5 +7 =12 加法 情况2 情况2 情况1 :无进位加法 0101 0101 进位carry 1010 进位carry 0100 + 0111 XOR 0111 |--> XOR 0010 |--> XOR 1000 -------- -------- | -------- | -------- 1100 0010 -- 1000 ---- 1100
在有进位的情况下,若发生进位,则对应的位上a和b的二进制值均为1。利用与运算可以求解到进位的数值。由于要进位,因此再将与操作的结果向左移动一位即可。即 carry = (a&b)<<1。
得到进位数值,就可以转换为 情况1:无进位的加法 求解。
综上,求解思路可以总结为
异或求解无进位情况下的和,sum = a^b(情况1)
判断进位 carry,若不为0,则为情况2,carry = (a&b)<<1,问题转化为了求解 carry 和 sum的和
Solution
递归函数实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public : int getSum (int a, int b) if (b==0 ) return a; int sum = a^b; int carry = (a&b)<<1 ; return getSum(sum,carry); } }; class Solution {public : int getSum (int a, int b) return (b==0 )? a: getSum(a^b,(a&b)<<1 ); } };
迭代实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public : int getSum (int a, int b) int carry; while (b){ carry = a & b; a = a ^ b; b = carry <<1 ; } return a; } };
520. 检测大写字母 Description
给定一个单词,你需要判断单词的大写使用是否正确。
我们定义,在以下情况时,单词的大写用法是正确的
1. 全部字母都是大写,比如"USA"。
2. 单词中所有字母都不是大写,比如"leetcode"。
3. 如果单词不只含有一个字母,只有首字母大写,比如 "Google"。否则,我们定义这个单词没有正确使用大写字母。
示例 1
输入: "USA"
输出: True示例 2
输入: "FlaG"
输出: False注意: 输入是由大写和小写拉丁字母组成的非空单词。
Approach 1-ASCII码值 Analysis 使用字母的ASCII值进行判断。
大写字母的ASCII值范围是65~90,小写字母的ASCII值范围是97~122。
总结判断逻辑如下
若字母长度为1,直接返回 true
如果(第一个字母小写) 或者 (第一个字母大写且第2个字母小写),若后续字母全部小写,则符合条件,大写使用正确
如果前2个字母大写,若后续字母全部大写,则符合条件,大写使用正确
Solution
Java 实现1: 使用 charAt(index) 实现
Java中,charAt(index) 函数可以返回字符串中指定索引值处(index)的字母,函数返回类型是 char。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution public boolean detectCapitalUse (String word) int wordLength = word.length(); if (wordLength == 1 ){ return true ; } if (word.charAt(0 ) >= 97 || (word.charAt(0 ) <= 90 && word.charAt(1 ) >= 97 )){ for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (word.charAt(i) <= 90 ){ return false ; } } } else { for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (word.charAt(i) >= 97 ){ return false ; } } } return true ; } }
Java 实现2: 使用 codePointAt(index) 实现
Java中,codePointAt(index) 函数可以返回字符串中指定索引值处(index)字母的ASCII值,函数返回类型是 int。
1 2 3 4 String word = "LiuBaoshuai" ; char myChar = charAt(word[3 ]); Character.codePointAt(word,3 );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public class Solution public boolean detectCapitalUse (String word) int wordLength = word.length(); if (wordLength == 1 ){ return true ; } if (Character.codePointAt(word,0 ) >= 97 || (Character.codePointAt(word,0 ) <= 90 && Character.codePointAt(word,1 ) >= 97 )){ for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (Character.codePointAt(word,i) <= 90 ){ return false ; } } } else { for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (Character.codePointAt(word,i) >= 97 ){ return false ; } } } return true ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public : bool detectCapitalUse (string word) int wordLength = word.length(); int codeFirst = (int )word[0 ]; if (wordLength == 1 ){ return true ; } if (codeFirst <= 90 ){ if ((int )word[1 ] <= 90 ){ for (int i=2 ;i<wordLength;i++){ int code = (int )word[i]; if (code >= 97 ){ return false ; } } } else { for (int i=2 ;i<wordLength;i++){ int code = (int )word[i]; if (code <= 90 ){ return false ; } } } } else { for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ int code = (int )word[i]; if (code <= 90 ){ return false ; } } } return true ; } };
Approach 2-直接使用内置大小写判断函数 Analysis 也可以直接使用语音内置的大小写判断函数实现。
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution public boolean detectCapitalUse (String word) int wordLength = word.length(); if (wordLength == 1 ) return true ; if (Character.isLowerCase(word.charAt(0 )) || (Character.isUpperCase(word.charAt(0 )) && Character.isLowerCase(word.charAt(1 )))){ for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (Character.isUpperCase(word.charAt(i))) return false ; } } else { for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (Character.isLowerCase(word.charAt(i))) return false ; } } return true ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public : bool detectCapitalUse (string word) int wordLength = word.length(); if (wordLength <= 1 ){ return true ; } if (islower (word[0 ]) || (isupper (word[0 ]) && islower (word[1 ]))){ for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (isupper (word[i])){ return false ; } } } else { for (int i=1 ;i<wordLength;i++){ if (islower (word[i])){ return false ; } } } return true ; } };
Approach 3-正则匹配实现 Analysis 总结判断逻辑如下
若字母长度为1,直接返回 true
如果(第一个字母小写) 或者 (第一个字母大写且第2个字母小写),若后续字母全部小写,则符合条件,大写使用正确
如果前2个字母大写,若后续字母全部大写,则符合条件,大写使用正确
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 public class Solution public boolean detectCapitalUse (String word) return word.matches("[A-Z]+|[a-z]+|[A-Z][a-z]+" ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class Solution public boolean detectCapitalUse (String word) return word.equals(word.toUpperCase()) || word.equals(word.toLowerCase()) || Character.isUpperCase(word.charAt(0 )) && word.substring(1 ).equals(word.substring(1 ).toLowerCase()); } }
292. Nim 游戏 Description
你和你的朋友,两个人一起玩 Nim 游戏:桌子上有一堆石头,每次你们轮流拿掉 1-3 块石头。 拿掉最后一块石头的人就是获胜者。你作为先手。
你们是聪明人,每一步都是最优解。
编写一个函数,来判断你是否可以在给定石头数量的情况下赢得游戏。
示例
输入: 4
输出: false
解释: 如果堆中有 4 块石头,那么你永远不会赢得比赛;
因为无论你拿走 1 块、2 块 还是 3 块石头,最后一块石头总是会被你的朋友拿走。Approach 1-数值分析 Analysis
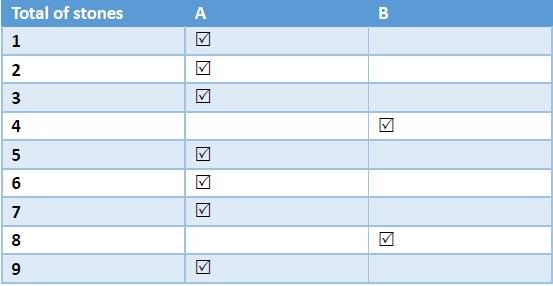
如上图所示
当石头总数为4时,A(先取者)一定是会输的;
当石头总数为5/6/7时,如果A首先拿走1/2/3个石头,那么B将面对剩下4个石头的情况,转化为了情况1,此时B一定是会输的;
当石头总数为8个时,无论A首先拿走几个,B都可以留下4个石头给A,转化为情况1,因此A一定是会输的;
当石头总数为9/10/11个时,A可以首先拿走1/2/3个,给B留下8个石头,转化为情况3,此时B一定是会输的
从上述分析可以看到,当有一方面对的石头数目是4个或者4的倍数,那么他一定是会输的。
Solutiuon
1 2 3 4 5 class Solution public boolean canWinNim (int n) return (n%4 != 0 ); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution {public : bool canWinNim (int n) return (n%4 != 0 ); } };
197. 上升的温度(SQL) Description
给定一个 Weather 表,编写一个 SQL 查询,来查找与之前(昨天的)日期相比温度更高的所有日期的 Id。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 + | Id(INT) | RecordDate(DATE) | Temperature(INT) | + | 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 | | 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 | | 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 | | 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 | +
例如,根据上述给定的 Weather 表格,返回如下 Id:
1 2 3 4 5 6 + | Id | + | 2 | | 4 | +
Approach 1-DATEDIFF实现 Analysis DATEDIFF(A,B) 函数可以返回 A 和 B 之间的天数
1 2 DATEDIFF('2007 -12 -31 ','2007 -12 -30 '); # 1 DATEDIFF('2010 -12 -30 ','2010 -12 -31 '); # -1
本题中,查询的条件有2个
与之前的日期相差为 1
比之前的温度高
Solution 1 2 3 SELECT b.IdFROM Weather as a,Weather as bWHERE a.Temperature < b.Temperature and DATEDIFF (a.RecordDate,b.RecordDate) = -1 ;
Approach 2-TO_DAYS实现 Analysis TO_DAYS(A) 函数返回了第0年和第A年之间的天数
Solution 1 2 3 SELECT b.IdFROM Weather as a,Weather as bWHERE a.Temperature < b.Temperature and TO_DAYS (b.RecordDate) - TO_DAYS (a.RecordDate) = 1
136. 只出现一次的数字 Description
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
说明
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗?示例 1
输入: [2,2,1]
输出: 1示例 2
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]
输出: 4Approach 1-异或实现 Analysis 使用异或XOR实现。将数组中所有的数值进行XOR操作,出现2次的数进行异或返回值是0,不会影响最后的结果。
因此,如果 N 是只出现一次的数字的话
1 2 3 4 N1 ^ N1 ^ N2 ^ N2 ^..............^ Nx ^ Nx ^ N = (N1^N1) ^ (N2^N2) ^..............^ (Nx^Nx) ^ N = 0 ^ 0 ^ ..........^ 0 ^ N = N
Solution
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution public int singleNumber (int [] nums) int length = nums.length; if (length==1 ){ return nums[0 ]; } else { for (int i=1 ;i<length;i++){ nums[0 ] = nums[0 ] ^ nums[i]; } } return nums[0 ]; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution {public : int singleNumber (vector <int >& nums) int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ;i<nums.size();i++){ result = result ^ nums[i]; } return result; } };